
The GMAT Exam - WHAT IS THE GMAT?
The GMAT, or Graduate Management Admission Test, is a computer-based standardised test, which is the part of the MBA application process, and is sat by over 240,000 graduates every year. Global business schools refer to GMAT Exam scores in their admission processes , and it is possible to sit the GMAT Exam in over 100 countries.
During the COVID pandemic, graduates have been permitted to sit the exam from home, as of 20 April 2020, under central supervision. You can take the GMAT up to eight times, and five times within a single year – as long as there is an 16-day break between attempts.
Note, however, that it costs approximately $250 to sit the exam.
The results are valid for five years.
The GMAT Exam
The GMAT Exam - How is the GMAT organised?
You will sit four papers, namely :
|
Paper
|
Number of question
|
Allotted time
|
|---|---|---|
|
Quantitative reasoning
|
31
|
62 minutes
|
|
Verbal reasoning
|
36
|
65 minutes
|
|
Integrated reasoning
|
12
|
30 minutes
|
|
Analytical writing
|
I essay
|
30 minutes
|
The GMAT Exam thus lasts for three hours seven minutes.
The GMAT Exam is a computer-adaptive test. This means that each section starts with an “average” question, and if you get it right, the next question will be more difficult. If at some point, you fail to answer a question correctly, the computer will adjust the level of difficulty and make the succeeding question easier. The harder the questions you answer, the higher your score.
The GMAT Exam – questions are based on the skills highlighted by businesses and academics as essential to effective management, so the GMAT Exam is not a test of knowledge, but a test of how you can apply information and reach decisions and conclusions. Critical thinking, communication and reasoning are as important as mathematical ability. Essentially, the GMAT Exam only has two types of questions: data sufficiency and problem-solving. Like all exams, practice is key to success…
The GMAT Exam - Quantitative Reasoning Paper
For the GMAT Exam you will not be permitted to bring your own calculator, but will be provided with laminated graph paper and a pen to use by the test centre.
The aim of this section is to determine whether you can solve quantitative problems, evaluate information and extract relevant facts from graphs. Algebra, geometry, rules, order, sets, ratios, percentages and arithmetic are core skills, along with algebraic and non-algebraic equalities. Data sufficiency is a major feature of the questions you will be answering – which, simply put, consists of deciding whether there is enough information available to answer a question.
The Quantitative Reasoning paper is combined with the Verbal Reasoning, in order to calculate a total score for the GMAT Exam.
The GMAT Exam - Verbal Reasoning Paper
The GMAT Exam – Verbal Reasoning Paper – This paper is divided into three themes:
- reading comprehension critical reasoning
- correcting sentence
The passages you will be given will vary in length and will test your ability to use grammar correctly, to make and assess an argument, create a plan of action and use logic to evaluate stated and inferred ideas. The Verbal Reasoning score is combined with the Qualitative Reasoning score to calculate the overall score in the GMAT Exam.
The GMAT Exam - Integrated Reasoning Paper
The GMAT Exam – Integrated Reasoning Paper – You will be given a calculator for this paper.
Integrated Reasoning tests whether you can assess data from a broad range of sources and from different formats and find a relationship between data and text. Each question may incorporate a number of sub-questions and you may be presented with a graph or table, multi-source, or two-part analysis. You could be offered a number of yes/no and true/false choices, or have to fill in blanks by using a pull-down menu. Multi-source reasoning is presented on tabs, which could include texts, charts, or tables. Two-part analysis has two com
The GMAT Exam - Analytical Writing Paper
The GMAT Exam – Analytical Writing Paper – You will be required to write an essay, based on the analysis of an argument.
This is not an opportunity to express your own views, but a chance to demonstrate good syntax, logical organization and development of ideas, and critical thinking.
Concentrate on considering what has been said, and evaluating the content. The examiner is looking for excellent communication skills and a strong structure to the essay.
You will be scored from 0-6:
|
6
|
Outstanding
|
|
5
|
Strong
|
|
4
|
Adequate
|
|
3
|
Limited
|
|
2
|
Flawed
|
|
1
|
Inadequate
|
The GMAT Exam Scoring
At the end of the GMAT Exam, you will see your Total Score displayed on the screen.
You will have two minutes to decide whether or not to accept or reject the test scores. Even if you decide to accept the score, you can still cancel it in the next 72 hours. Similarly, if you decide to go ahead and reject it, you can reinstate it over the next four years and eleven months.
The Total Score is based on how well you did in the Verbal Reasoning and Qualitative Reasoning Papers, and also gives you your score for the Integrated Reasoning section. The Official Score, which you can get a few weeks later, includes the Analytical Writing result. Your score will fall between 200 and 800, which is a cumulative score based on a percentile ranking. The table, below, shows how the number of correct answers you give is converted into the final score.
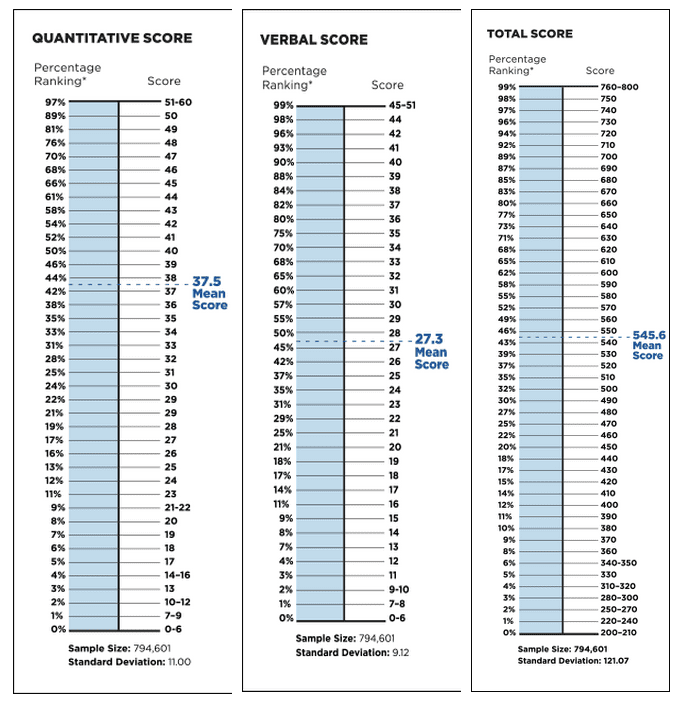

It has been calculated that 30 people a year get a perfect 800!
And only six per cent of applicants score over 700.
Three factors play a major part in the GMAT Exam scoring:
- How many answers were correct
- How many questions you answered
- The level of difficulty of the questions
GMAT preparation courses
Take the GMAT exam preparation course and you show that you're able to work or study effectively in an English-speaking environment.
What GMAT score do I need to get accepted to a leading business school to do my MBA?
The following table, from 2019, illustrates the average score of accepted applicants and the general GMAT range at 10 leading business schools.
|
Institution
|
Average score
|
Range of GMAT Scores
|
|---|---|---|
|
Stanford
|
732
|
600-790
|
|
Harvard
|
730
|
610-800
|
|
INSEAD
|
709
|
570-780
|
|
U.Penn Wharton
|
732
|
500-790
|
|
London Business School
|
708
|
600-780
|
|
MIT Sloan
|
728
|
690-760
|
|
Yale
|
730
|
690-760
|
|
Oxford University, Said
|
690
|
510-800
|
|
HEC Paris
|
690
|
600-770
|
|
IESE
|
686
|
600-750
|
What is the next step if I wish to sit the GMAT and apply for an MBA course?
Elab runs a series of workshops and individual one-on-one sessions, which prepare candidates for both the GMAT and the GRE tests. Our programme is based on analysing your strengths and weaknesses and working through each of the GMAT papers, teaching you the techniques which will help you maximise your score. Our experienced tutors will make sure you are comfortable and familiar with the format, know what to expect and how to approach each paper and answer questions in what is a very rigid and demanding time frame.
Contact Elab to book a free consultation. We are here to help you on your journey towards gaining an MBA at a globally-renowned business school.
Call or drop us an email and we will organise a consultation.
What do you think about Elab's help?











